Andrii Yalanskyi/iStock via Getty Images
Tesla Is Struggling
The hype surrounding electric vehicles (EVs) is cooling down. While EV sales soared in 2021 and 2022, there are multiple examples of that growth slowing significantly. Some analysts point to a substantial decline in EV stock prices, with certain companies experiencing serious revenue declines in the past year. This could indicate a more cautious market outlook on the short-term trajectory of the electric car adoption.
Tesla, Inc. (NASDAQ:TSLA), as a front-runner of the revolution in the automotive industry, is in the midst of a tough battle in terms of vehicle prices, tough competition, lower-than-expected demand, falling margins, and all the issues characterizing an industry with terrible economics. Moreover, Tesla just missed earnings expectations big time with the biggest revenue decline YTD since 2012.
Little over a year ago, I posted an article, “Tesla And Terrible Business Economics,” presenting a bearish thesis for the company and its midterm future. The piece remains valid one year later, and the EV maker has dropped 27.93% since then, being currently the worst-performing stock YTD in the S&P Index (SP500). CEO Elon Musk keeps painting a futuristic vision of a world dominated by renewable sources of energy and alternative ways of powering vehicles. Yet, the reality looks different, especially considering regions other than Silicon Valley, the New York metropolitan area, or a few other wealthy parts of the world.
Tesla is not the one and only EV maker anymore. The competition keeps pace in the race and fights an equal fight for the consumer. The pricing power for the Texas-based car manufacturer doesn’t exist anymore. Yet, revenues and profits grow. The controversial CEO who has done miracles is still in charge, although a bit distracted with X – formerly Twitter. Are the industry risks, combined with company-specific issues and most of all, high valuation, worth the reward an investor may reap by investing in Tesla today? Probably not, and several solid arguments support the bearish thesis on the American EV maker.
Tesla’s Shrinking Margins: No Pricing Power
When an industry with a reputation for difficult economics meets a manager with a reputation for excellence, it is usually the industry that keeps its reputation intact.
– Warren Buffett.
What characterizes the auto industry is high competition, which forces manufacturers to contend ferociously for a customer. This leads to comparable prices of vehicles offering similar features and performance levels. Conversely, this causes profitability metrics of various carmakers in the same narrow range. Tesla is a good example of this phenomenon. Once the EV hype faded, so did the company’s margins. Tesla’s gross margin for Q4 2023 was 17.6%, the lowest since 2019, down more than 600 basis points from the year before.
Gross Profit Margin of Tesla vs. Toyota vs. Ford vs. GM vs. Volkswagen (Seeking Alpha)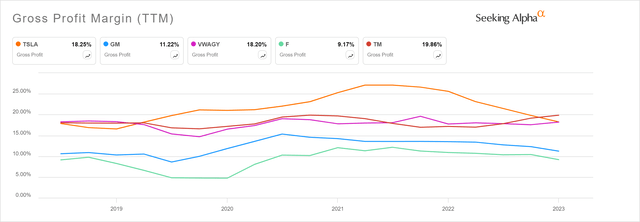
Tesla once enjoyed record-breaking profit margins, reaching as high as 25.6% in FY 2022. However, a succession of price reductions has led to a decline in its previously celebrated profitability, causing concern among investors as they approach more typical levels.
EV Transaction Price (Kelly Blue Book)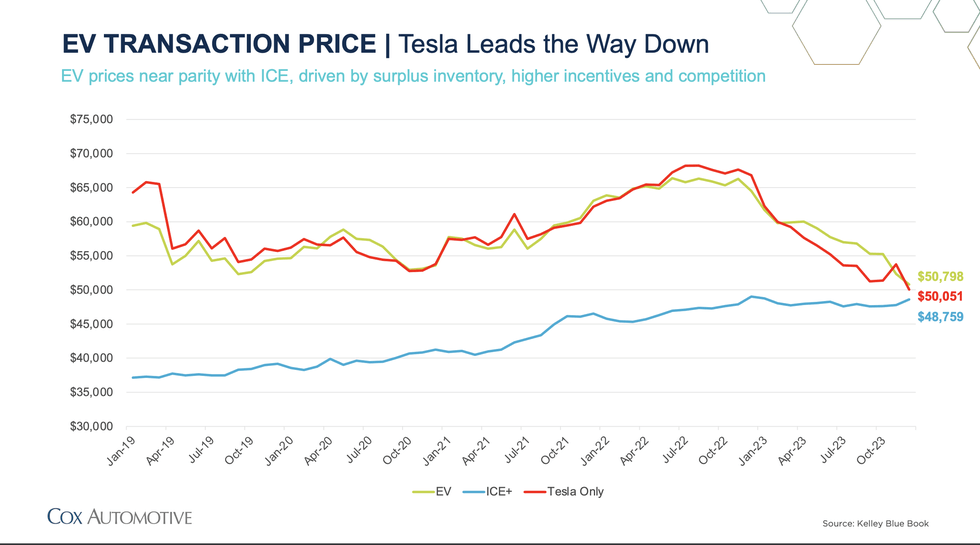
By now, it should have become clear that Tesla is a car company, generating over 85% of its revenues from the automotive segment. Since the company has matured, its vehicle prices have come down and margins have followed, currently trailing Toyota Motor Corporation (TM). Within a year, between January 2023 and January 2024, the price of the best-selling model in the new EV market – the Tesla Model Y plunged over 21% – tumbled from nearly $63,000 to less than $50,000. In contrast, the differences in transaction prices among Tesla’s competitors were in the low single digits.
On April 20th, 2024, nearly two weeks after releasing numbers of its deliveries, Tesla again slashed the prices of its vehicles Y, S, and X by $2,000 in the U.S. This move just reaffirmed the current trend and doesn’t give much hope that it will reverse soon.
The consequence of these price cuts is not only the decline of margins, but also lower sales and earnings numbers. These have just been seen in the reported Q1 results, with revenues down 9% YTD from $25.17 billion last year to $21.3 billion. Earnings per share plummeted 53% to $0.34 from $0.73 a year ago.
Tesla Facing Fierce Competition
BYD Outsells Tesla
In the electric vehicle market, a thrilling competition is unfolding between Tesla and BYD Company Limited (BYDDF). Tesla, once the undisputed champion, now faces a relentless challenger in the Chinese automaker BYD. BYD has stormed ahead in global sales, outselling Tesla in the crucial fourth quarter of 2023 with 526,000 battery electric vehicles (BEVs) compared to Tesla’s 484,500. While Tesla still holds the crown for the full year 2023 with a record-breaking 1.8 million EVs delivered, BYD is catching up rapidly, selling over 1.57 million BEVs, with six vehicles in the top ten best-selling EVs globally in 2023.
There is a strategic difference between the two competitors: Tesla focuses on premium, high-performance vehicles with a starting price of around $46,000 for the Model 3, while BYD offers a wider range of models at more accessible price points, responding to the surging demand for affordable EVs. This is particularly significant in China, the world’s largest car market, with high price sensitivity.
Volkswagen Takes Over Tesla in Germany
Volkswagen AG (VWAGY), the legacy automaker generating the highest revenue among car manufacturers, held 4.6% of the global EV market share in 2023. Although the company sells much fewer electric cars than Tesla (0.77 million units sold compared to Tesla’s 1.80 million in 2023), the German behemoth expects dynamic growth in 2024 due to new editions of some of its best-selling models, and also by updating its EV portfolio.
The ID.4 and ID.5 have recently undergone significant updates, featuring a completely updated operating concept and drive system. Additionally, Volkswagen is set to introduce the new ID.7 Tourer, the variant of its flagship all-electric model, the ID.7, later this year. Moreover, Tesla may soon feel the competition from Volkswagen in the U.S. market. In response to the increasing demand for SUVs, the German manufacturer plans to produce a fully electric SUV in the high-volume A-segment starting in 2026. This will be a direct competitor to the Tesla Model X. It’s worth noting that 81% of cars sold by Volkswagen in the U.S. in 2023 were SUVs.
In Germany, Volkswagen surpassed the U.S. automaker as the leading electric car brand with 70,628 new registrations in 2023, an increase of almost 12%. Tesla experienced a nine percent decline with 63,685 new registrations, although the American company’s Model Y remained the most popular EV model ahead of VW’s IDs.
Other Tesla Competitors Don’t Sleep, Either
Established automakers like Ford Motor Company (F), which closed a record EV sales year with the F-150 Lightning becoming the best-selling electric pickup, and General Motors Company (GM), which announced planned EV investments worth $35 billion, are present in the EV space with competitive offerings. Their initiatives are further squeezing Tesla’s market share. To maintain its position, Tesla will have to adapt by potentially introducing more affordable models, optimizing production costs, and defending its technological edge, none of which is easy in the automotive industry, known as an industry with terrible economics. The coming years will be a test of Tesla’s ability to adapt in a rapidly evolving EV space. Yet, Tesla does remain innovative, competitive, and efficient and there are no signs it’s backing off from its mission.
It took us 12 years to build the first million, and about 18 months to the second million. The third million, 11 months. Then less than seven months to build the 4 millionth.
– Senior Vice President Tom Zhu at the Tesla 2024 Investor Day.
EV Hype Collapse
During the Q1 FY2024, Tesla delivered 386,810 all-electric vehicles, marking a 9% decrease compared to the previous year. The numbers were met with a major disappointment among investors. Despite this decline, Tesla remained the leader in EV sales, with no other automotive group surpassing its numbers. BYD, which has a different customer base, experienced a moderate 13% growth year-over-year, reaching 300,114 EV deliveries in Q1.
Meanwhile, Volkswagen Group also faced challenges in passenger all-electric car sales, with Q1 results totaling 136,136 units, down approximately 3% from the previous year.
Summary of all-electric car sales in Q1 ‘2024 (YoY):
- Tesla: 386,810 (down 9%).
- BYD: 300,114 (up 13%).
- Volkswagen Group: 136,136 (down 3%).
Tesla vs. BYD vs. Volkswagen All-Electric Vehicle Sales (InsideEVs)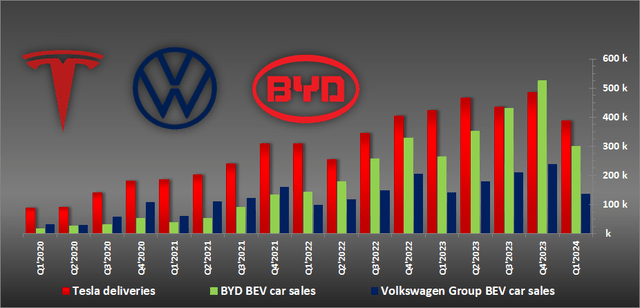
The slowdown in EV sales is attributed to various factors, including consumer concerns, supply chain disruptions, and economic uncertainties. Despite a surge in EV production, sales are slowing. Consumers are hesitant due to cost, range anxiety, and lack of charging infrastructure. This has led to a glut of EVs on dealer lots.
While government incentives push for electrification, and billions of dollars are being committed by automakers (over $616 billion by 2027) consumer demand seems to be wavering, leading to an oversupply of EVs in the market. According to Cox Automotive’s Industry Insights 2024 report, the automotive industry ended 2023 with an EV inventory equivalent to 113 days, contrasting with the more typical 69 days for ICE vehicles, which includes hybrids.
With relative optimism about the future of electric vehicles, concerns remain about the current state of the market. Used EV prices have seen significant declines, indicating potential challenges in EV resale value and overall market demand. However, some argue that this decline may be temporary and not indicative of a broader slowdown in EV adoption.
It’s worth noting that the used EV market is young and constantly evolving, presenting some uncertainties. Battery life and its impact on resale value are still being understood. Future policy changes, particularly regarding tax credits, can also significantly affect the market. Additionally, anxieties about the availability and reliability of public charging infrastructure persist for many potential EV buyers.
The expectations for EV growth in the U.S. market have shifted from ‘rosy to reality’ as sales increase, but customer acceptance of EVs isn’t keeping pace.”
Cox Automotive noted in its 2024 forecast report.
The industry’s EV strategy may change significantly in the coming months, driven by political pressures. Proposed increases in fuel economy standards could result in substantial fines for automakers, potentially exceeding $14 billion collectively. The potential role of hybrids and plug-in hybrids in meeting these regulations remains unknown, as the standards were designed with rapid EV adoption in mind.
Besides that, the upcoming U.S. presidential election also poses risks to the industry, with potential implications for fuel economy mandates. In Europe, stricter EV regulations aim to phase out traditional fossil-fuel vehicles by 2035, though there have been calls to reconsider or drop this ban.
Tesla’s Valuation
Tesla And Its Elevated Earnings Multiple
Many investors, especially from the retail crowd, look at Tesla’s revenues and extrapolate them into the future. This approach might work in some cases. However, applying it to a company with such a short history of profitability, and such an unpredictable path forward considering all the risks and obstacles mentioned in the article, the result may get skewed significantly.
First, the past doesn’t indicate the future, and it’s crucial to keep it in mind when investing in anything. Secondly, there are hints in the company’s financials on why this approach might lead to inaccuracies.
One of the indications worth keeping an eye on in terms of Tesla’s sales is a discrepancy between its revenue growth and revenue per share growth.
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| Revenue Growth | 28 % | 71 % | 51 % | 19 % |
| Revenue per Share Growth | 22 % | 61 % | 43 % | 17 % |
In the last four years, Tesla kept diluting its investors. However, the differences have been decreasing, which is a positive development.
Moreover, Tesla’s EPS growth plummeted from 676% in FY 2021 to 19% in FY 2023. Currently, analysts are estimating a fairly sluggish EPS increase of 8.41% CAGR over the next 3-5 years. At first glance, it seems much too low for a company whose P/E ratio is 34.2
P/E GAAP of Tesla vs. Volkswagen vs. Ford vs. GM vs. BYD (Seeking Alpha)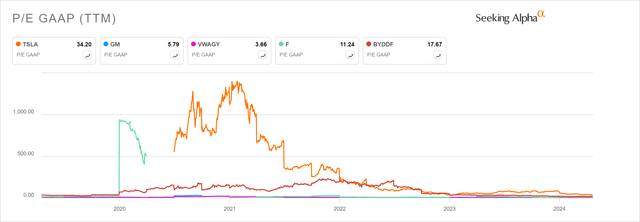
Compared to four other competitors, Tesla seems to be far ahead of itself in terms of the stock price, since it doesn’t justify current growth. The valuation exceeds the typical range for companies in the automotive industry. Even contrasting Tesla with its fiercest competitor BYD, the Texas-based manufacturer looks two times more expensive on a P/E basis.
Analyst Estimates on Tesla
According to analyst estimates, Tesla will earn $16.16 per share in 2033. By applying earnings predictions for the company from now until 2033, the following valuation model can be built.
Tesla Discounted Earnings Model – Analyst Estimates (Author – Data: Seeking Alpha)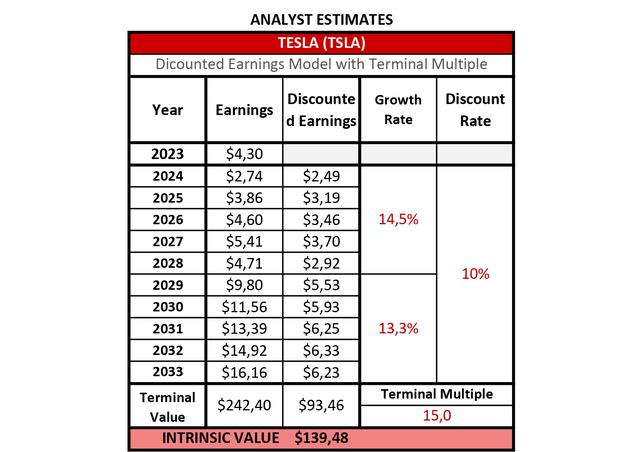
One can see that Tesla is assumed to grow 14.5% CAGR in the first five years and only slightly less in the following five. A terminal multiple of 15 was applied, which corresponds with a long-term market average. It might be seen as very conservative by those who see Tesla conquering the world with its technological solutions beyond electric cars and solar systems. For those who consider the company a car manufacturer, this P/E ratio will be very optimistic. However, by sticking to the long-term market average, Tesla looks fairly valued right now, as the stock price is hovering around $140.0 per share as of April 22, 2024.
Normal Case for Tesla
In the normal case, a growth of 8.4% CAGR for the next 10 years is assumed. If this scenario materializes, Tesla’s stock price is likely ahead of itself.
Tesla Discounted Earnings Model – Normal Case (Author – Data: Seeking Alpha)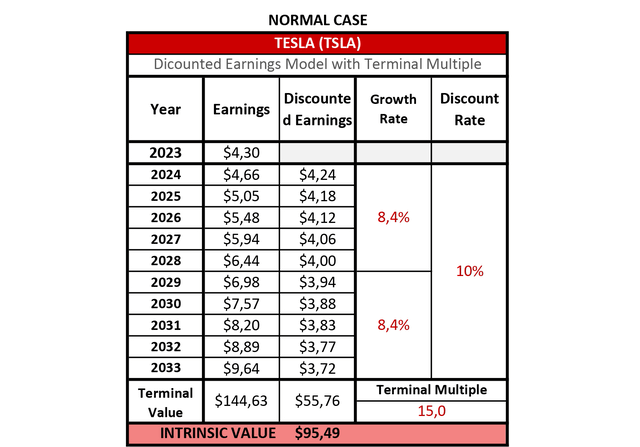
A share price of $95.49 might seem very low for many. Yet, the fact that Tesla stock was on an enormous run, fueled by the post-pandemic EV hype, could indicate that a lot got priced in. While many EV companies, such as NIO Inc. (NIO), Rivian Automotive, Inc. (RIVN), and Mullen Automotive, Inc. (MULN) are hitting new all-time-lows or Fisker Inc. (FSRN) being on the verge of bankruptcy, Tesla is still holding up. Yet, if the normal case scenario became real, and Tesla delivered such EPS numbers over the next 10 years, the company would be overvalued by 47.7%.
Tesla’s Earnings
The sentiment around Tesla ahead of its Q1 2024 earnings was dull. Missing delivery numbers induced disappointment among investors, which could be seen from the beginning of the year, sending the stock 42.7% down YTD.
Besides that, Tesla confirmed layoffs affecting over 10% of its global workforce, recalled more than 3,000 Cybertruck vehicles, and has just cut prices of its cars again. That’s not the best setup before the earnings. Any miss may send the stock price sharply lower.
Tesla disappointed investors by missing the estimates and reporting significantly lower numbers YTD:
- Earnings per share: $0.45 adjusted vs. expected $0.51 per share.
- Revenue: $21.30 billion vs. $22.15 billion expected.
The revenue decline was influenced by several factors, including a decline in the average selling price of vehicles compared to the previous year, along with an unfavorable mix impact. Additionally, there was a reduction in vehicle deliveries, partly due to disruptions in production at the Fremont factory and Giga Berlin, as well as a negative currency exchange impact.
However, there were areas of growth in other parts of the business, and an increase in Full Self-Driving (“FSD”) revenue recognition YTD, attributed to the release of the Autopark feature in North America.
Despite this, operating income also decreased YTD to $1.2 billion, leading to a 5.5% operating margin. This decline was primarily due to factors such as reduced vehicle ASP, increased operating expenses related to AI and R&D projects, the expenses related to the Cybertruck production ramp, and lower vehicle deliveries causing updates and disruptions.
Yet, on a positive note, there were mitigating factors, including a decrease in cost per vehicle, growth in gross profit in Energy Generation and Storage, and higher FSD revenue recognition resulting from the Autopark feature release.
Tesla May Surprise Everybody Again
Tesla is facing a wave of challenges – stricter regulations, the Cybertruck recall, price cuts due to competition, and a global slowdown in demand. To navigate these hurdles, Tesla will need to execute efficiently at the highest level. Having Elon Musk and a highly innovative work culture might help beat the odds and deliver stronger-than-expected performance across its segments.
Price cuts and competition demand advanced strategies. First, Tesla needs to focus on cost reduction through production efficiencies and supply chain optimization. Second, the company must start appealing to a broader range of customers who can’t afford vehicles from the premium price segment. Moreover, fast expansion of the Supercharger network, monetization of software features, and data-driven services can create new revenue streams.
A global demand slowdown demands geographic expansion into new markets with high EV adoption and less competition. This could be achieved with a more affordable Tesla model or a strong certified pre-owned program.
Competition can be tackled by staying ahead in battery technology, autonomous driving, and other innovative features. Prioritizing exceptional customer service could be the cherry on top which would encourage potential buyers to go for a Tesla vehicle.
Beyond these immediate challenges, Tesla could increase investments in exploring opportunities in battery storage solutions or renewable energy products. There are, of course, unknown potential revenue streams that might be in the making while being kept highly confidential.
Tesla’s history suggests it’s comfortable taking risks and pushing boundaries. If some of Elon Musk’s visions materialize and Tesla becomes the pioneer in other technological segments, the company should be back on the fast lane and generate high growth again. Yet, there are a lot of question marks and unknowns in this rosy scenario. Thus, it’s difficult to quantify it and make any reasonable predictions.
Conclusion
Tesla’s challenges appear to be mounting, with investors expressing disappointment as the stock plummeted nearly 42.7% YTD. This decline follows a series of events that have been unfolding for roughly a year and was confirmed in the newly reported quarterly numbers. Falling margins, strong competition, low demand, and a general slowdown in the EV market only confirm that no matter how innovative and well-run a company is, it will finally get hit by the reality of the industry it’s in. And if the industry has terrible economics, the odds are against the company.
Besides that, internal issues from confirming significant layoffs, a recall of the Cybertruck, as well as cutting vehicle prices, have been affecting the automaker. All these developments reflect a broader picture of uncertainty surrounding Tesla’s future trajectory, as it navigates regulatory, financial, and operational hurdles in the fiercely competitive electric vehicle market.
On top of all that, Tesla seems to be overvalued, and its stock is prone to a further decline in the current environment. Valuation will finally matter. Tesla stock might be currently in the process of being reevaluated by market participants. Unless the leadership doesn’t announce breaking news bringing back euphoria, the near-term future will probably remain rough for Tesla and its investors.
Editor’s Note: This article discusses one or more securities that do not trade on a major U.S. exchange. Please be aware of the risks associated with these stocks.
